VITREO RETINAL SERVICES
Retina is the most important light sensitive layer ,located inside of eye, sending impulses to the brain for vision.The retina acts like the film role of a camera.
Sudden loss of vision, gradual loss of vision ,floaters, blurring of vision, flashes of light in one or both eyes, reduce or loss the visual field, you should schedule an appointment with an ophthalmologist especially Vitreo retinal consultant or surgeon to get your eyes checked immediately.
Shankar’s eye hospitals offering best Equipped Vitreo Retinal speciality department with experienced Vitreo retinal surgeon . All Vitreo retinal surgeries are performed here like Retinal detachment or other Retinal disorders like Macular hole, Vitreous Haemorrhage’s etc.
We have micro-incisional vitrectomy system (MIVS).

Retinal Disorders Treated
1. Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy occurs secondary to deterioration of blood vessels in the retina as a complication of diabetes mellitus. The breakdown of retinal blood vessels may result in fluid leaking into the center of the retina (macular edema) or abnormal blood vessel formation on the surface of the retina (neovascularization) which can bleed and scar, resulting in loss of central and possibly peripheral vision.
- NPDR
- PDR
- HRPDR
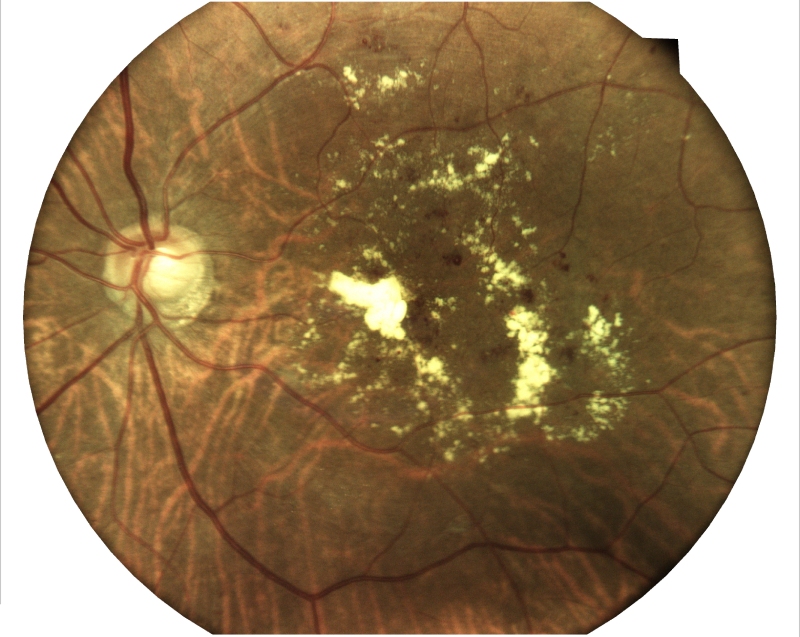
2. Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a common, complex, degenerative condition affecting people aged 60 years and above causing vision loss, which results in difficulty to read, drive, or see someone’s face on progression to more advanced stages. Genetical and Smoking , Vitamin deficiency are the reasons.
3. Retinal Vein Occlusion
Retinal vein occlusion is a blockage in the ocular blood vessel that can result in vision loss. The retinal veins carry away used blood from the retina and when one of these veins is blocked, the used blood cannot drain away, which causes swelling and haemorrhage (bleeding). CRVO and BRVO are commonly seen.
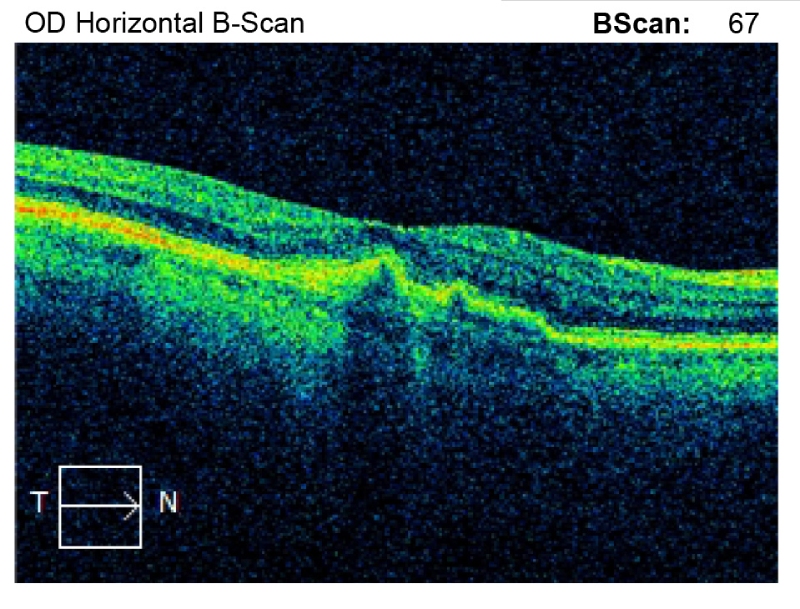
4. Central Serous Chorioretinopathy (CSCR)
CSCR is a condition that causes fluid to accumulate in the centre of the retina (Macula). Fluid leaks from the blood vessel layer under the retina called the choroid. It is more common in men and typically occurs between the ages of 25 to 50 years. Most patients have a blurred spot in the centre of vision. Objects often appear distorted and miniature in size. The main reasons are sleeplessness , strain etc.
5. Retinal Detachment
Retina the nerve layer of eye separates from its normal position, causing sudden loss of vision, Common reasons are Mature cataract, High Myopia, Trauma
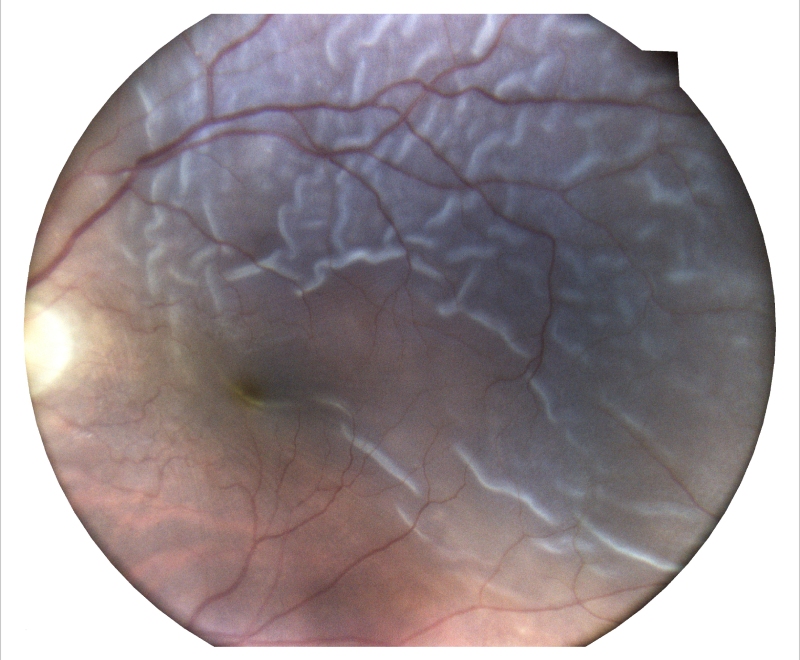
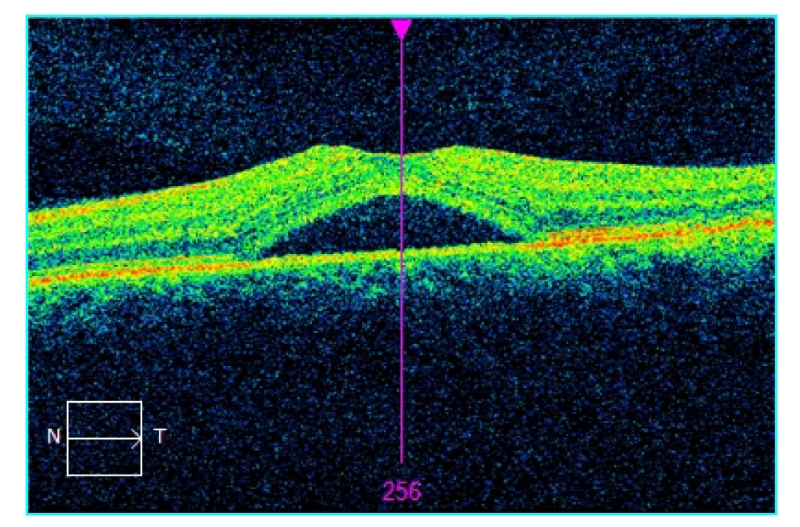
6. Macular Hole
Macular hole (MH) is a retinal break commonly involving the fovea, centre of the retina. Distorted vision, straight line might be curvy or wavy. Risk factors include age, female gender, myopia, trauma, and ocular inflammation.
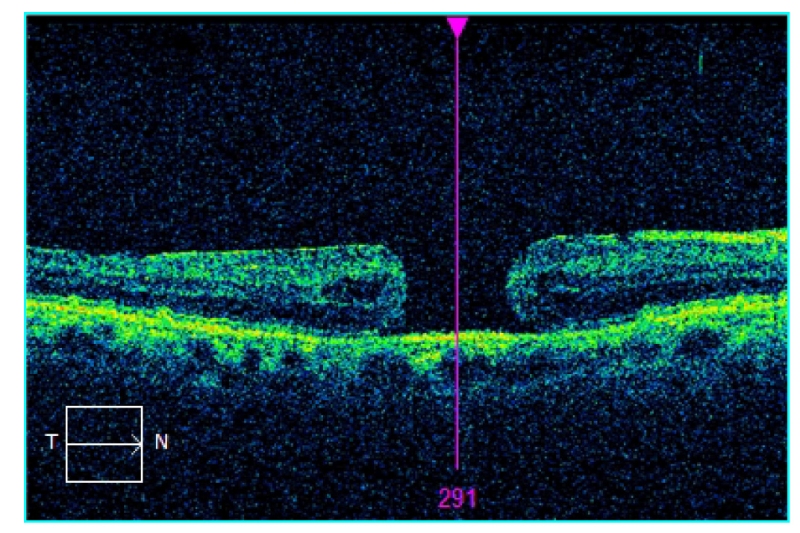
7. Vitreous Hemorrhage
Vitreous haemorrhage is a relatively common cause of sudden loss of vision, leakage of blood into the vitreous humour of the eye. The most common causes include proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) with or without retinal tear, and ocular trauma.
8. Intra Ocular Foreign Body (IOFB)
IOFBs are foreign bodies inside the eye globe. IOFBs can cause perforating or penetrating injuries. It is Critical Ophthalmic emergency. The visual prognosis depends on the zone of injury, type, and size of the foreign body, and the subsequent complications.
9. Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP)
It is a retinal condition that affects premature babies and causes abnormal development of the retinal blood vessels. If not diagnosed and treated early, it can lead to complete blindness.
10. Posterior Vitreous Detachment (PVD)
PVD is a natural change that occurs during adulthood, when the vitreous gel that fills the eye separates from the retina. The most common cause is aging, but you can have PVD in your 40s, particularly if you’re short-sighted, if your eye has been injured, or if you’ve had previous eye surgery.
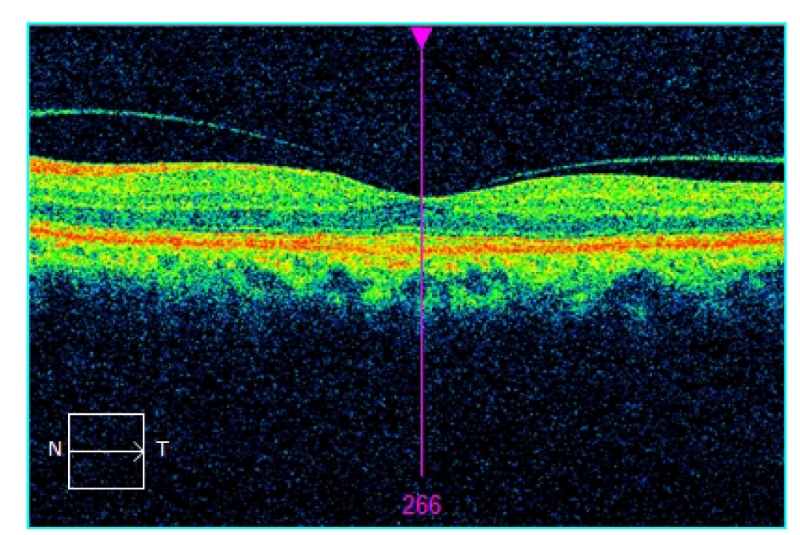
11. High Myopia
Refractive error of the eye more than minus 6 diopter. It leads to pathologic myopia which increases the risk of several vision-threatening conditions like cataract, glaucoma, and retinal detachment.
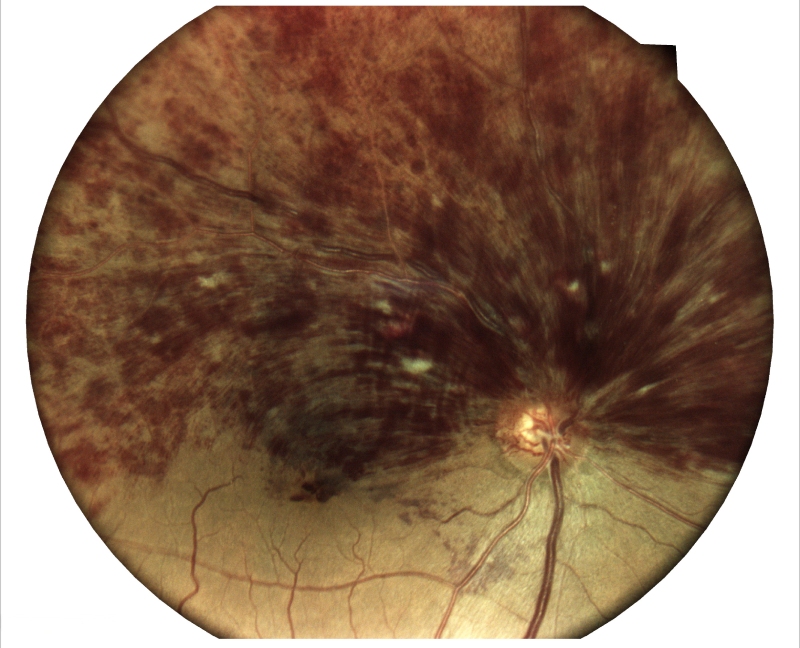
12. Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP)
RP is a group of inherited eye disorders that gradually deteriorate the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. This degeneration leads to progressive vision loss, often beginning with night blindness and peripheral vision loss. While RP has no cure, early diagnosis and expert care can significantly preserve vision and enhance quality of life.
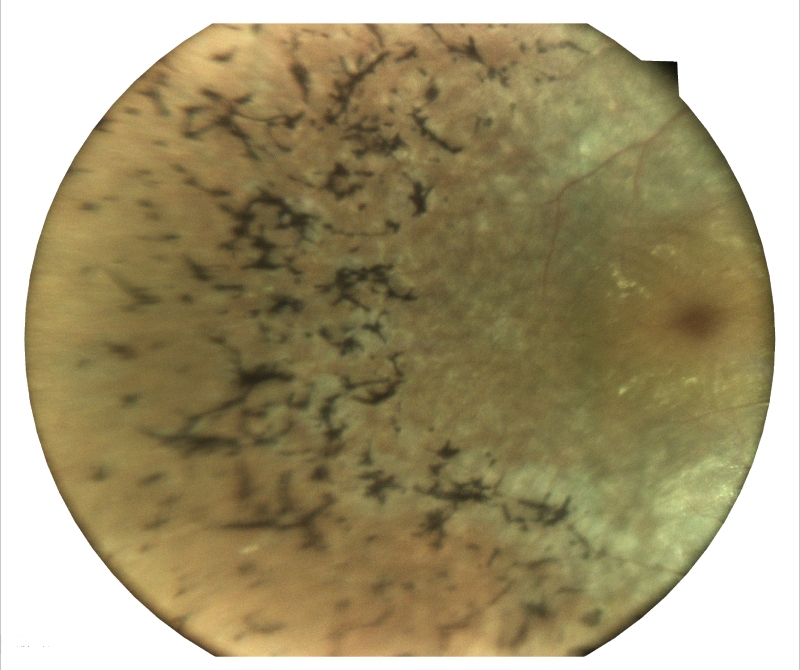
Retinal Diagnostics
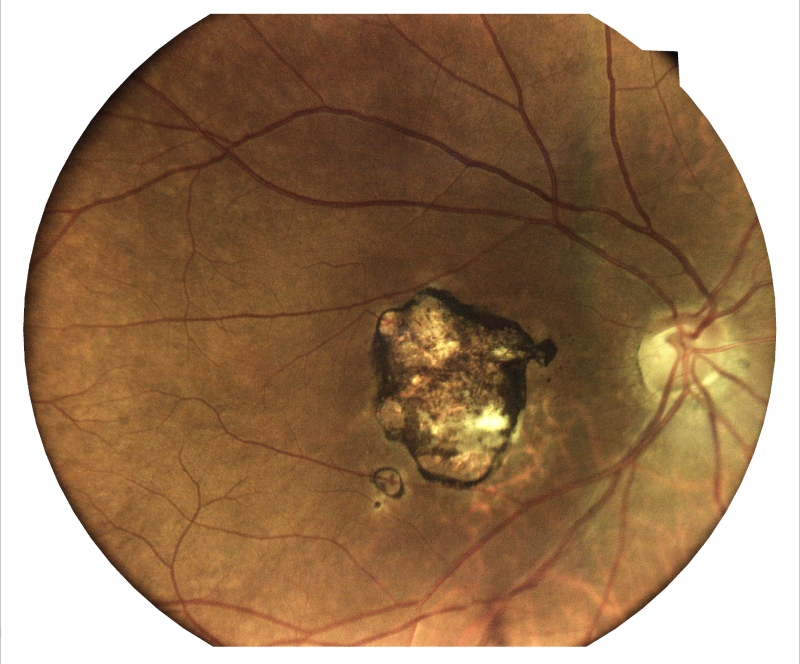
Fundus Photography
Fundus photography, also known as retinal photography, is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure that captures detailed images of the back of the eye, known as the fundus. These images provide valuable insights into the overall health of the retina, optic nerve, macula, and blood vessels, enabling early detection and treatment of various eye conditions.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a revolutionary imaging technique that has transformed the way eye doctors diagnose and manage a wide range of eye conditions. This non-invasive procedure provides high-resolution, cross-sectional images of the retina, the innermost layer of the eye, and other internal eye structures.
OCT at Shankar’s Eye Hospital: We offer the latest Zeiss OCT technology and expertise to provide our patients with the most accurate and up-to-date diagnosis and treatment plans.
Ultrasonography
Ultrasonography, also known as an eye ultrasound, is a painless and non-invasive diagnostic tool that utilizes high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images of the internal structures of the eye. This versatile technique plays a crucial role in evaluating a wide range of eye conditions, particularly in RD, VH, IOFBs, tumor, and penetrating injury, providing valuable insights for diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring disease progression particularly in opaque media.
Treatment Options
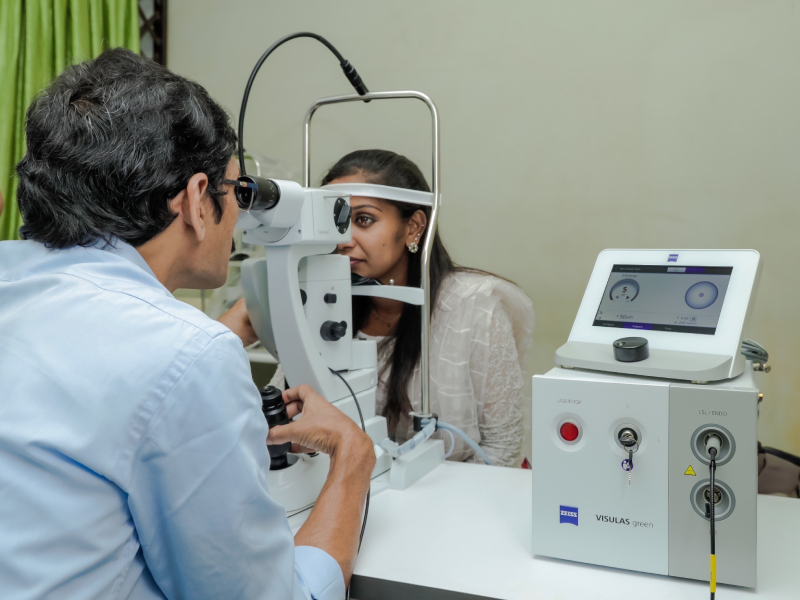
Laser Photocoagulation
Laser photocoagulation, a minimally invasive procedure, utilizes a concentrated beam of light to treat various eye conditions, including diabetic retinopathy, retinal thinning (high myopic), and retinal tears. At Shankar’s Eye Hospital, our skilled vitreo-retinal specialists employ laser photocoagulation with precision and care to preserve and enhance vision. Here we use Zeiss Visuals Green Laser Machine.
Panretinal Photocoagulation (PRP)
Laser is a treatment for certain eye conditions that involves using a laser to seal off abnormal blood vessels in the retina.
Indications:
- Moderate or severe NVD
- Mild NVD or NVE if associated with preretinal or vitreous hemorrhage
- Patients with severe proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) in the other eye
Focal Laser
Focal laser photocoagulation is a procedure that treats macular edema and small breaks in the retina.
Indications:
- CSME
Barrage Laser
Barrage laser is a laser procedure to strengthen the weak regions of the retina. A person’s retina may weaken due to significant conditions such as myopia (nearsightedness).
Indications:
- Preventive treatment for conditions like retinal detachment and retinal tears
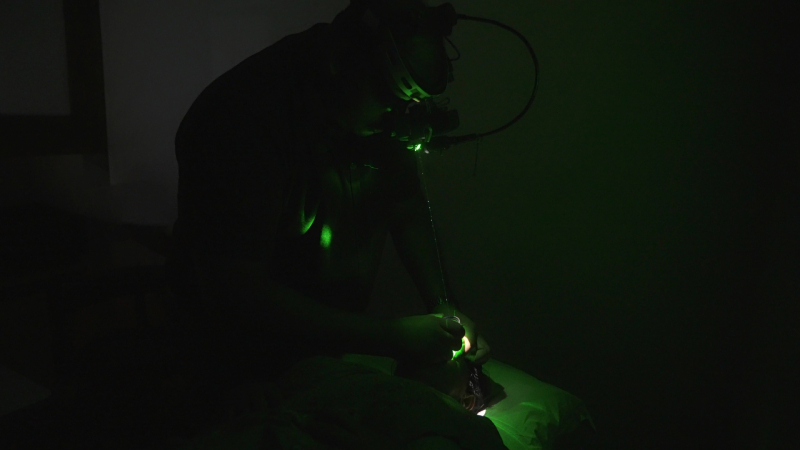

Benefits of Laser Photocoagulation
- Minimally Invasive: Laser photocoagulation is an outpatient procedure, meaning you can go home the same day. It requires no incisions or stitches, minimizing discomfort and recovery time.
- Targeted Treatment: The laser beam precisely targets specific areas of the retina, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
- Preservation of Vision: Laser photocoagulation effectively prevents vision loss or further deterioration in many eye conditions.
Anti-VEGF Intravitreal Injection Treatment
Indications:
- Diabetic macular edema/PDR
- Wet ARMD
- Idiopathic Juxtafoveolar Retinal Telangiectasis
- High Myopes With CNVM
- Choroidal Rupture With CNVM
- CRVO and BRVO with NVE
Injection Site
Superotemporally or inferotemporally for ease of access, though any quadrant can be used.
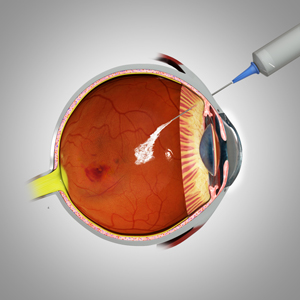
Intravitreal Injections
Wide range of Intra vitreal Anti Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (anti-VegF) injections available:
- Razumab (Ranibizumab)
- Accentrix (Ranibizumab)
- Eylea (aflibercept)
- Ozurdex (Dexamethasone)
- IVTA (Intravitreal Triamcinolone Acetonide)
- Intra vitreal antibiotics
Post-operative instructions following your injection
- You should not rub your injected eye. . You should not wash your face and hair or shower for 48 hours
- You should not rub your injected eye. . You should not wash your face and hair or shower for 48 hours
- Please continue to use any other eye drops you are currently using, which were prescribed by your ophthalmology doctor
- Please use a fresh bottle of these drops for the injected eye
- Strictly adhere to your appointment visit
Retinal Surgery
Retinal surgery encompasses a range of procedures aimed at repairing or reattaching the retina. The type of surgery depends on the specific condition and severity of the retinal detachment. Common retinal surgery procedures include:
Vitrectomy
A more complex procedure that involves removing the vitreous gel, the clear substance filling the space between the lens and the retina, to access and repair damaged retinal tissue.
Membrane Peeling
Delicate procedure that involves removing the thin, fibrous tissue that may form on the surface of the retina.
Endo Laser
Utilizes laser energy to treat the retina internally during a vitrectomy.
Silicon Oil Insertion (SOI)
Procedure where silicon oil is injected into the eye to hold the retina in place after surgery.
Silicon Oil Removal (SOR)
The process of removing the silicon oil from the eye after it has served its purpose in retinal surgery.
Pneumatic Retinopexy
A minimally invasive procedure that involves injecting a gas bubble into the vitreous cavity to push the detached retina back into place.
At Shankar’s Eye Hospital, our team of experienced vitreo-retinal surgeons is committed to providing the highest quality care for patients with retinal disorders. Our surgeons utilize the latest advancements in retinal surgery techniques and technologies, ensuring optimal outcomes for our patients.
